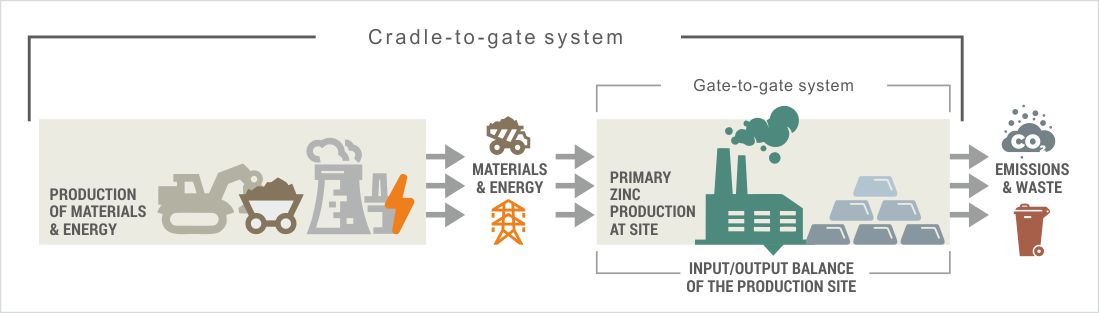
HZL conducted Life Cycle Assessment (LCA) study as per ISO 14040/44 standard, using the approach of “cradle to grave” for their Zinc, Lead and Silver products. This study establishes the baseline impact of '1 ton of Zinc, Lead and Silver Production' for facilities of Hindustan Zinc Limited. The system boundary for this study is a cradle to grave system.
The exercise aims to understand the various environmental impacts of the selected products as well as evaluate the savings potential which can then further be used for setting sustainability targets or communication to the stakeholders. LCA is helping us in:
 |
Identifying all potential areas for improvement and direct efforts so as to reduce the impact, or otherwise minimise as far as possible, getting the consequent environmental improvement and compare with the benchmark and
best available technologies |
 |
Optimisation and improvement of the production processes, end-of-life scenarios, etc. |
 |
Stimulating the generation of information on the life cycle performance of materials to support both reductions in the footprint of the upstream activities to harvest the materials, as well as more sustainable applications of materials in products |
 |
Competing materials who are putting environmental information on their products into the marketplace through
a variety of mechanisms |
 |
Objectively analysing different future scenarios and possible alternatives, and their implications and impact on the life cycle |
 |
Third party standards and rating schemes that are trying to improve the environmental footprint of product and building systems |
This study provides a platform to understand the environmental profile across the value chain for three product systems from various routes and different sites. Life cycle inventory and impact assessment results can be used to perform internal benchmarking. HZL may initiate the external benchmarking with the best available technologies on various key impact indicators. Outcome of the LCA study can be utilised to communicate to the customers, downstream/end users, policy makers, NGOs and other stakeholders to showcase environmental performance of products of HZL.
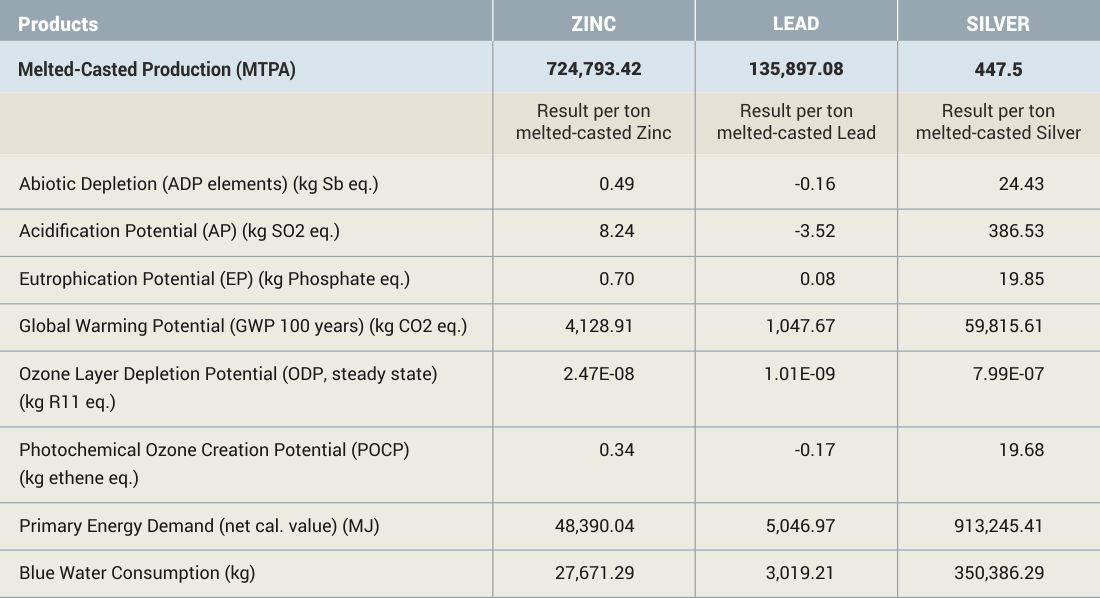
RESULTS
A set of life cycle environmental impact indicators such as Abiotic Depletion of Fossil Elements, Acidification Potential, Eutrophication Potential, Global Warming Potential, Ozone Layer Depletion Potential, Photochemical Ozone Creation Potential, Primary Energy Demand and Blue Water Consumption were considered.
While comparing the results with the study undertaken by International Zinc Association and International Lead Association, HZL's results are at par with the world average data. Unlike European manufacturers having lower grid emission factor for electricity generation, HZL's production processes are dependent on coal-based electricity production. In spite of this situation, the LCA results are quite close to world average.
We have enhanced the renewable energy portfolio, implemented many projects and initiatives for waste reduction and recycling, while various water and energy saving projects have largely contributed in reducing the overall impact of all the operations.